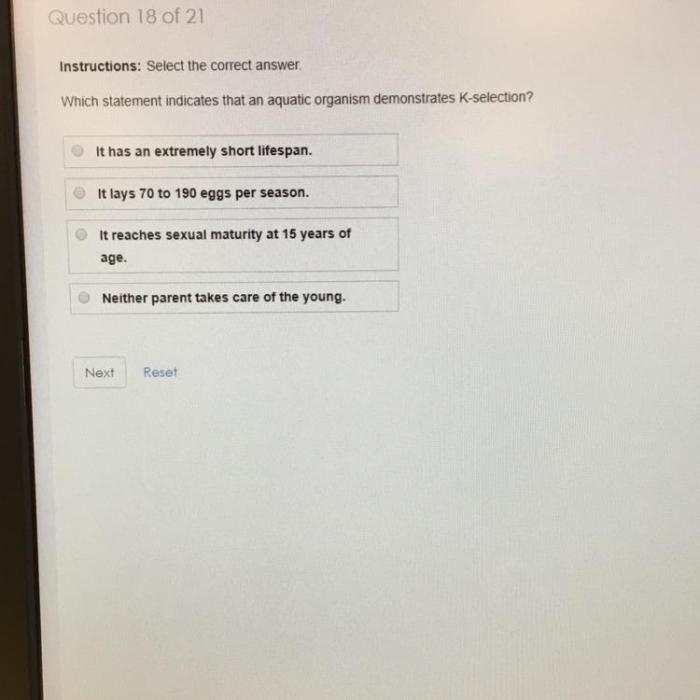
Which statement indicates that an aquatic organism demonstrates k-selection? This question delves into the fascinating realm of life history strategies in aquatic environments, where organisms have evolved unique adaptations to thrive in diverse and dynamic habitats. K-selection, a reproductive strategy characterized by slow growth, late maturity, and long lifespans, plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and resilience of aquatic ecosystems.
This article explores the characteristics, life history strategies, and environmental factors that favor the evolution of k-selection in aquatic organisms, providing insights into the intricate adaptations that shape their survival and success.
K-selected aquatic organisms exhibit distinct life history traits that enable them to persist in stable and predictable environments. Their slow growth rates and extended lifespans allow them to accumulate resources and experience, increasing their chances of survival and reproductive success.
Late maturity ensures that individuals have sufficient time to acquire the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate their complex environment. Additionally, k-selected organisms typically produce a small number of well-developed offspring, investing significant parental care to enhance their survival and competitive abilities.
Characteristics of K-Selection in Aquatic Organisms
K-selection, a reproductive strategy, refers to organisms that have evolved in stable, predictable environments with limited resources. In aquatic environments, K-selected organisms exhibit traits such as:
- Slow growth rates
- Late maturity
- Long lifespans
- Production of few, well-developed offspring
- High parental care
These traits enable K-selected organisms to maximize their reproductive success in environments where resources are limited and competition is intense.
Life History Strategies of K-Selected Aquatic Organisms: Which Statement Indicates That An Aquatic Organism Demonstrates K-selection
K-selected aquatic organisms typically exhibit the following life history strategies:
- Slow growth rates:This allows them to conserve energy and allocate resources towards other essential functions, such as reproduction and survival.
- Late maturity:K-selected organisms reach sexual maturity at a later age, which allows them to attain a larger size and increase their chances of survival before reproducing.
- Long lifespans:These organisms have evolved to live for extended periods, which increases their reproductive potential over time.
These strategies contribute to the stability of aquatic ecosystems by ensuring that populations are maintained at a relatively constant level.
Reproductive Strategies of K-Selected Aquatic Organisms
K-selected aquatic organisms employ specific reproductive strategies to enhance the survival and success of their offspring:
- Producing few, well-developed offspring:K-selected organisms invest heavily in each offspring, ensuring their survival and competitive advantage.
- High parental care:Parents provide extensive care and protection to their offspring, increasing their chances of survival and development.
These reproductive strategies maximize the fitness of offspring and contribute to the overall success of the species in stable environments.
Environmental Factors Influencing K-Selection in Aquatic Organisms
The evolution of K-selection in aquatic organisms is influenced by several environmental factors:
- Stable and predictable habitats:These habitats provide consistent resources and minimize environmental fluctuations, allowing organisms to adopt K-selected strategies.
- Limited resources:In environments with limited resources, competition for survival is intense, favoring organisms that prioritize reproductive success over rapid population growth.
These environmental factors shape the life history and reproductive strategies of aquatic organisms, leading to the evolution of K-selection in stable and resource-limited environments.
Examples of K-Selected Aquatic Organisms
Numerous aquatic organisms exhibit K-selection traits, including:
- Sea turtles:Slow-growing, long-lived, and produce a small number of offspring with high parental care.
- Sharks:Late maturity, long lifespans, and produce few, well-developed offspring.
- Deep-sea fish:Adapted to stable, low-resource environments, exhibiting slow growth rates and long lifespans.
These organisms have evolved K-selected traits to optimize their reproductive success and survival in their respective aquatic environments.
Query Resolution
What are the key characteristics of k-selected aquatic organisms?
K-selected aquatic organisms are characterized by slow growth rates, late maturity, long lifespans, and a small number of well-developed offspring with high parental care.
How do k-selected aquatic organisms contribute to the stability of aquatic ecosystems?
K-selected organisms play a vital role in maintaining the stability of aquatic ecosystems by ensuring the long-term survival of populations and contributing to the overall biodiversity and resilience of the ecosystem.
What are some examples of k-selected aquatic organisms?
Examples of k-selected aquatic organisms include sea turtles, sharks, deep-sea fish, and certain species of corals.